I fail to understand some options in the dumpBackup.php maintenance script of Mediawiki.
What is the effect of --include-files? In my test wiki, dumpBackup.php --current --include-files and dumpBackup.php --current both contain the pages of the File: namespace and I see no difference.
What is the effect of --uploads? In my test wiki I see that the xml file contains a tiny bit more of xml but, to me, it looks like this is all information which is there already as part of the File: page. What is the use of this flag?
When I add both --include-files and --uploads I get the next surprise. I actually expected the combined effect of both options, but what I get is the file content of the uploaded files and the upload record. Why did I not get the file contents when I used --include-files alone?
When I use only --include-files and --uploads but no --current I would have expected to get the content of the uploaded files and the upload record (and none of the other pages). However ,I get the warning no valid action specified and no further information at all
I am completely confused since I do not understand the logic behind all of this.
Software: Octave v7.1.0
There seems to be no option of defining the page size while doing publish ("FILE", "pdf") . The manual for pdf is: 11.11.1 docs.octave/.../Publish.
It's kinda surprising as it's a one word addition to the output TeX file : a4paper. I can do this manually each time I publish but being able to specify it somehow within the publish function would be awesome.
Surprisingly, there are plenty options for specifying page size in figures and images. Search for papertype at: 15.3.3.2 docs.octave/.../Figure-Properties
I searched with "Matlab" and found this page, and it fetched the results for "Matlab Report Generator" mlreportgen which seems a different thing.
I'd be interested to listen about other ways of doing it automatically too (like adding that word in TeX file via shell scripting and text string manipulation maybe).
As directed by #cris-luengo in the pointer comment to the linked manual, one solution can be to edit (or create) the function files (to used by the publish function) with the desired changes to specify the paper size.
The function files location can be found by:
opening the function file in octave gui and then proceeding from there:
edit (fullfile (fileparts (which ("publish")), "private", "__publish_html_output__.m"))
or, executing the following in octave REPL/command line:
fullfile (fileparts (which ("publish")), "private")
There, among other files, 2 files will be:
__publish_html_output__.m
__publish_latex_output__.m
Edit the _latex_ containing file to add ,a4paper (or other predefined size in latex) alongwith 10pt in the line '\documentclass[10pt]{article}',, optionally with a comment in a proceeding newline as a reminder that you added it, something like: '% Modification: specify a4paper',
If pdf format were directly specified as a new function file, then I'd have preferred to modify its copy and calling that directly in publish(), but since the publish pdf eventually calls publish latex, so, the only option at hand in this method seems to edit the original publish latex function file itself.
Is there any way to render LaTex in README.md in a GitHub repository? I've googled it and searched on stack overflow but none of the related answers seems feasible.
For short expresions and not so fancy math you could use the inline HTML to get your latex rendered math on codecogs and then embed the resulting image. Here an example:
- <img src="https://latex.codecogs.com/gif.latex?O_t=\text { Onset event at time bin } t " />
- <img src="https://latex.codecogs.com/gif.latex?s=\text { sensor reading } " />
- <img src="https://latex.codecogs.com/gif.latex?P(s | O_t )=\text { Probability of a sensor reading value when sleep onset is observed at a time bin } t " />
Which should result in something like the next
Update: This works great in eclipse but not in github unfortunately. The only work around is the next:
Take your latex equation and go to http://www.codecogs.com/latex/eqneditor.php, at the bottom of the area where your equation appears displayed there is a tiny dropdown menu, pick URL encoded and then paste that in your github markdown in the next way:
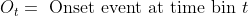
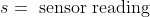
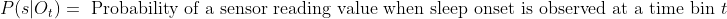
I upload repositories with equations to Gitlab because it has native support for LaTeX in .md files:
```math
SE = \frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}
```
The syntax for inline latex is $`\sqrt{2}`$.
Gitlab renders equations with JavaScript in the browser instead of showing images, which improves the quality of equations.
More info here.
Let's hope Github will implement this as well in the future.
My trick is to use the Jupyter Notebook.
GitHub has built-in support for rendering .ipynb files. You can write inline and display LaTeX code in the notebook and GitHub will render it for you.
Here's a sample notebook file: https://gist.github.com/cyhsutw/d5983d166fb70ff651f027b2aa56ee4e
Readme2Tex
I've been working on a script that automates most of the cruft out of getting LaTeX typeset nicely into Github-flavored markdown: https://github.com/leegao/readme2tex
There are a few challenges with rendering LaTeX for Github. First, Github-flavored markdown strips most tags and most attributes. This means no Javascript based libraries (like Mathjax) nor any CSS styling.
The natural solution then seems to be to embed images of precompiled equations. However, you'll soon realize that LaTeX does more than just turning dollar-sign enclosed formulas into images.
Simply embedding images from online compilers gives this really unnatural look to your document. In fact, I would argue that it's even more readable in your everyday x^2 mathematical slang than jumpy .
I believe that making sure that your documents are typeset in a natural and readable way is important. This is why I wrote a script that, beyond compiling formulas into images, also ensures that the resulting image is properly fitted and aligned to the rest of the text.
For example, here is an excerpt from a .md file regarding some enumerative properties of regular expressions typeset using readme2tex:
As you might expect, the set of equations at the top is specified by just starting the corresponding align* environment
**Theorem**: The translation $[\![e]\!]$ given by
\begin{align*}
...
\end{align*}
...
Notice that while inline equations ($...$) run with the text, display equations (those that are delimited by \begin{ENV}...\end{ENV} or $$...$$) are centered. This makes it easy for people who are already accustomed to LaTeX to keep being productive.
If this sounds like something that could help, make sure to check it out. https://github.com/leegao/readme2tex
Since May 2022, this has been officially supported:
Inline:
Where $x = 0$, evaluate $x + 1$
Blocks:
Where
$$x = 0$$
Evaluate
$$x + 1$$
One can also use this online editor: https://www.codecogs.com/latex/eqneditor.php which generates SVG files on the fly. You can put a link in your document like this:
 which results in:
.
I test some solution proposed by others and I would like to recommend TeXify created and proposed in comment by agurodriguez and further described by Tom Hale - I would like develop his answer and give some reason why this is very good solution:
TeXify is wrapper of Readme2Tex (mention in Lee answer). To use Readme2Tex you must install a lot of software in your local machine (python, latex, ...) - but TeXify is github plugin so you don't need to install anything in your local machine - you only need to online installation that plugin in you github account by pressing one button and choose repositories for which TeXify will have read/write access to parse your tex formulas and generate pictures.
When in your repository you create or update *.tex.md file, the TeXify will detect changes and generate *.md file where latex formulas will be exchanged by its pictures saved in tex directory in your repo. So if you create README.tex.md file then TeXify will generate README.md with pictures instead tex formulas. So parsing tex formulas and generate documentation is done automagically on each commit&push :)
Because all your formulas are changed into pictures in tex directory and README.md file use links to that pictures, you can even uninstall TeXify and all your old documentation will still works :). The tex directory and *.tex.md files will stay on repository so you have access to your original latex formulas and pictures (you can also safely store in tex directory your other documentation pictures "made by hand" - TeXify will not touch them).
You can use equations latex syntax directly in README.tex.md file (without loosing .md markdown syntax) which is very handy. Julii in his answer proposed to use special links (with formulas) to external service e.g . http://latex.codecogs.com/gif.latex?s%3D%5Ctext%20%7B%20sensor%20reading%20%7D which is good however has some drawbacks: the formulas in links are not easy (handy) to read and update, and if there will be some problem with that third-party service your old documentation will stop work... In TeXify your old documentation will works always even if you uninstall that plugin (because all your pictures generated from latex formulas are stay in repo in tex directory).
The Yuchao Jiang in his answer, proposed to use Jupyter Notebook which is also nice however have som drawbacks: you cannot use formulas directly in README.md file, you need to make link there to other file *.ipynb in your repo which contains latex (MathJax) formulas. The file *.ipynb format is JSON which is not handy to maintain (e.g. Gist don't show detailed error with line number in *.ipynb file when you forgot to put comma in proper place...).
Here is link to some of my repo where I use TeXify for which documentation was generated from README.tex.md file.
Update
Today 2020.12.13 I realised that TeXify plugin stop working - even after reinstallation :(
For automatic conversion upon push to GitHub, take a look at the TeXify app:
GitHub App that looks in your pushes for files with extension *.tex.md and renders it's TeX expressions as SVG images
How it works (from the source repository):
Whenever you push TeXify will run and seach for *.tex.md files in your last commit. For each one of those it'll run readme2tex which will take LaTeX expressions enclosed between dollar signs, convert it to plain SVG images, and then save the output into a .md extension file (That means that a file named README.tex.md will be processed and the output will be saved as README.md). After that, the output file and the new SVG images are then commited and pushed back to your repo.
I just published a new version of xhub, a browser extension that renders LaTeX (and other things) in GitHub pages.
Cons:
You have to install the extension once.
Pros:
No need to set up anything.
Just write Markdown with math
Display math:
```math
e^{i\pi} + 1 = 0
```
and line math $`a^2 + b^2 = c^2`$.
(Syntax like on GitLab.)
Works on light and dark background. (Math has text-color)
You can copy-and-paste the math just like text
As an example, check out this GitHub README:
You can get a continuous integration service (e.g. Travis CI) to render LaTeX and commit results to github. CI will deploy a "cloud" worker after each new commit. The worker compiles your document into pdf and either cuses ImageMagick to convert it to an image or uses PanDoc to attempt LaTeX->HTML conversion where success may vary depending on your document. Worker then commits image or html to your repository from where it can be shown in your readme.
Sample TravisCi config that builds a PDF, converts it to a PNG and commits it to a static location in your repo is pasted below. You would need to add a line that fetches pdfconverts PDF to an image
sudo: required
dist: trusty
os: linux
language: generic
services: docker
env:
global:
- GIT_NAME: Travis CI
- GIT_EMAIL: builds#travis-ci.org
- TRAVIS_REPO_SLUG: your-github-username/your-repo
- GIT_BRANCH: master
# I recommend storing your GitHub Access token as a secret key in a Travis CI environment variable, for example $GH_TOKEN.
- secure: ${GH_TOKEN}
script:
- wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/blang/latex-docker/master/latexdockercmd.sh
- chmod +x latexdockercmd.sh
- "./latexdockercmd.sh latexmk -cd -f -interaction=batchmode -pdf yourdocument.tex -outdir=$TRAVIS_BUILD_DIR/"
- cd $TRAVIS_BUILD_DIR
- convert -density 300 -quality 90 yourdocument.pdf yourdocument.png
- git checkout --orphan $TRAVIS_BRANCH-pdf
- git rm -rf .
- git add -f yourdoc*.png
- git -c user.name='travis' -c user.email='travis' commit -m "updated PDF"
# note we are again using GitHub access key stored in the CI environment variable
- git push -q -f https://your-github-username:$GH_TOKEN#github.com/$TRAVIS_REPO_SLUG $TRAVIS_BRANCH-pdf
notifications:
email: false
This Travis Ci configuration launches a Ubuntu worker downloads a latex docker image, compiles your document to pdf and commits it to a branch called branchanme-pdf.
For more examples see this github repo and its accompanying sx discussion, PanDoc example,
https://dfm.io/posts/travis-latex/, and this post on Medium.
I have been looking around and found that this answer in another question works best for me. i.e. use githubcontent math renderer, e.g. to display:
Use this link
Beware of the latex needs to be url encoded, but otherwise work quite well for me.
If you are having issues with https://www.codecogs.com/latex/eqneditor.php, I found that https://alexanderrodin.com/github-latex-markdown/ worked for me. It generates the Markdown code you need, so you just cut and paste it into your README.md document.
You may also take a look on my tool latexMarkdown2Markdown which convert LaTeX to SVG and generate a table of content with chapter numbering.
Good news!
According to this blogpost, now GitHub supports Mathjax in readme files.
You can use in-line LaTeX inspired syntax using $ delimiters, or in-blocks using $$ delimiters.
Writing inline expressions:
This sentence uses $ delimiters to show math inline:
$\sqrt{3x-1}+(1+x)^2$
Writing expressions as blocks:
The Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality
$$\left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k b_k \right)^2 \leq \left( \sum_{k=1}^n a_k^2
\right) \left( \sum_{k=1}^n b_k^2 \right)$$
Source: https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/writing-on-github/working-with-advanced-formatting/writing-mathematical-expressions
You can use markdowns, e.g.
=\beta_0&space;+&space;\beta_1&space;x&space;+&space;u)
Code can be typed here: https://www.codecogs.com/latex/eqneditor.php.
Edit: As germanium pointed out, it does not work for README.md but other git pages though no explanation is available.
My quick solution is this
step 1. Add latex to your .md file
$$x=\sqrt{2}$$
Note: math eqns must be in $$...$$ or \\(... \\).
step 2. Add the following to your scripts.html or theme file (append this code at the end)
<script type="text/javascript" async
src="https://cdn.mathjax.org/mathjax/latest/MathJax.js?config=TeX-MML-AM_CHTML">
Done!. See your eq. by loading the page.
We have a problem with info frame not giving the correct file-name and line-number.
We are using Tcl 8.6 with some code forked for proc and source, we are overriding source command with some custom code, so that some of the lines can be skipped, After this, info frame isn't working for this forked version.
Is there a solution for this?
Alas, if you override bits and pieces of code like that then you lose the file tracking. It's done by tracing identities of literals and it really doesn't like what you're up to there.
Formally, the file tracking is known to be theoretically flaky, but it doesn't seem to be much of a problem in practice unless you get into the level of processing that you're up to. One possible workaround is to do your preprocessing by changing files into other files (e.g., in a “deploy” directory) so that source and proc can stay conventional. (Doing that sort of copy is also pretty much what you do when you build an application; you've just got a filtering copy instead of a simple one.)
Details
The following two locations in Tcl's source contain the heart of the problem for you:
generic/tclProc.c lines 199–280, Tcl_ProcObjCmd()
generic/tclIOUtil.c, lines 1955–1959, TclNREvalFile() (and probably lines 1819–1823, Tcl_FSEvalFileEx() too, if you want to do file evaluation that's not source)
You want that code in tclProc.c to trigger so that the frame data is built for the procedure, but for that you need the trigger in tclIOUtil.c to set the triggering action. Your changes to proc and source block both of these. The info frame command reads the data that that block in tclProc.c generates.
Perhaps the easiest way — if you're building custom C in the first place — is to insert your processing in those two functions in tclIOUtil.c; I'd do it by calling a shared function that modifies the contents of the buffer in the Tcl_Obj passed in (which will be single-referenced at that point, and hence writable). Just… don't alter the number of newlines if you want the data out of info frame to be sensible.
I have two libraries libA and libB.
libA contains a file Action.h
libB contains a file action.h
I want to generate doxygen documentation in the same output directory for both libraries. This directory is to be used in Windows, for which action.html and Action.html is unfortunately considered to be the same file. To prevent this clash, I wish to render the generated files unique by prepending their path names to them.
Therefore, I set FULL_PATH_NAMES to YES.
I expect to see something like libA_Action.html and libB_action.html when I generate the documentation, but I don't! I still see Action.html and action.html. Its as if the FULL_PATH_NAMES parameter does nothing at all. Do I also need to set some other parameter in the Doxyfile to make the FULL_PATH_NAMES parameter work correctly?
You're probably running doxygen twice - one time for each library. If that is the case, doxygen isn't aware of the fact that it might clash with an output from another run, so when it find an existing file, it assumes that it is leftover from a previous run, and overrides it.
Setting FULL_PATH_NAMES doesn't help, as doxygen has no idea that multiple libraries exist, so, as far as doxygen is concerned, the prefix is identical to all files, so even when you adding a force it, it adds nothing (That's probably a bug).
The solution to your problem is setting both libraries as inputs to the same doxygen project.
You can do it by setting INPUT to multiple folders in the configuration file:
INPUT = ...bla\Lib1 \
...bla\Lib2